Trichloroethylene
CASRN 79-01-6 | DTXSID0021383
- IRIS Summary (PDF) (63 pp, 520 K)
- Supporting Documents for Trichloroethylene
On this page:
Noncancer Assessment
Reference Dose for Oral Exposure (RfD) (PDF) (63 pp, 520 K) Last Updated: 09/28/2011
| System | RfD (mg/kg-day) | Basis | PoD | Composite UF | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developmental, Immune | 5 x 10 -4 | (See Note) | High |
Note: The RfD was derived as a midpoint among three similar candidate RfDs—0.00048 mg/kg-day for decreased thymus weight in mice (Keil et al., 2009), 0.00037 mg/kg-day for developmental immunotoxicity (decreased PFC and increased delayed-type hypersensitivity) in mice (Peden-Adams et al., 2006), and 0.00051 mg/kg-day for fetal heart malformations in rats (Johnson et al., 2003). See Section I.A.1 of the IRIS Summary for Trichloroethylene for more information.
Reference Concentration for Inhalation Exposure (RfC) (PDF) (63 pp, 520 K) Last Updated: 09/28/2011
| System | RfC (mg/m3) | Basis | PoD | Composite UF | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developmental, Immune | 2 x 10 -3 | (See Note) | High |
Note: The RfC was derived as the midpoint of two similar candidate RfCs—0.0019 mg/m3 for decreased thymus weight in mice (Keil et al., 2009) and 0.0021 mg/m3 for fetal heart malformations in rats (Johnson et al., 2003). See Section I.B.1 of the IRIS Summary for Trichloroethylene for more information.
Cancer Assessment
Weight of Evidence for Cancer (PDF)
(63 pp, 520 K)
Last Updated: 09/28/2011
| WOE Characterization | Framework for WOE Characterization |
|---|---|
| Carcinogenic to humans (Combined route) | Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment (U.S. EPA, 2005) |
- Under the Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment (U.S. EPA, 2005), TCE is characterized as "carcinogenic to humans" by all routes of exposure.
- This may be a synopsis of the full weight-of-evidence narrative.
Quantitative Estimate of Carcinogenic Risk from Oral Exposure (PDF) (63 pp, 520 K)
Oral Slope Factor:
5.2
x 10-2
per mg/kg-day
Extrapolation Method: PBPK model-based route-to-route extrapolation of the inhalation unit risk estimate for kidney cancer with a factor of 5 applied to include non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) and liver cancer risks, combined risk, includes application of age-dependent adjustment factors (ADAFs).
Tumor site(s): Urinary, Hematologic, Hepatic
Tumor type(s): Renal cell carcinoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and liver tumors (Charbotel et al., 2006; EPA, 2011; Raaschou-Nielsen et al., 2003)
Note: EPA has concluded that trichloroethylene is carcinogenic by a mutagenic mode of action. Thus, based on the EPA cancer guidelines (2005), the oral slope factor (OSF) addressing lifetime exposure includes application of ADAFs. The OSF is recommended for lifetime exposures. EPA has also provided an adult-based cancer slope factor of 4.6 x 10-2 per mg/kg-day. This adult-based cancer slope factor can be used instead of the OSF when assessing cancer risk associated with exposure scenarios that don’t include early life (< 16 years of age) or when other calculations by the user are necessary (e.g., when applying ADAFs to age-specific exposure estimates).
Quantitative Estimate of Carcinogenic Risk from Inhalation Exposure (PDF) (63 pp, 520 K)
Inhalation Unit Risk:
4.8
x 10-6
per µg/m3
Extrapolation Method: Low-dose linear extrapolation from the point of departure (LEC01) with a factor of 4 applied to include non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) and liver cancer risks, combined risk, includes application of age-dependent adjustment factors (ADAFs).
Tumor site(s): Hematologic, Hepatic, Urinary
Tumor type(s): Renal cell carcinoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and liver tumors (Charbotel et al. 2006; EPA, 2011; Raaschou-Nielsen et al., 2003)
Note: EPA has concluded that trichloroethylene is carcinogenic by a mutagenic mode of action. Thus, based on the EPA cancer guidelines (2005), the inhalation unit risk (IUR) addressing lifetime exposure includes application of ADAFs. The IUR is recommended for lifetime exposures. EPA has also provided an adult-based cancer unit risk of 4.1 x 10-6 per µg/m3. This adult-based cancer unit risk can be used instead of the IUR when assessing cancer risk associated with exposure scenarios that don’t include early life (< 16 years of age) or when other calculations by the user are necessary (e.g., when applying ADAFs to age-specific exposure estimates).
Chemical Documents
Aug 2011: IRIS Toxicological Review of Trichloroethylene (Interagency Science Discussion Draft) (Report)
Dec 2009: IRIS Toxicological Review of Trichloroethylene (Interagency Science Consultation Draft) (Report)
Oct 2009: IRIS Toxicological Review of Trichloroethylene (TCE) (External Review Draft) (Report)
May 2006: Uncertainties In Trichloroethylene Pharmacokinetic Models (Other)
Jan 2002: Letter To The Editor: Carcinogenicity Of Trichloroethylene (Journal)
Feb 2001: Cytochrome P450-Dependent Metabolism Of Trichloroethylene In The Rat Kidney (Journal)
Other EPA Information
- Human Health Benchmarks for Pesticides (HHBP). This database provides human health benchmarks for pesticides that may be present in drinking water.
- Office of Pesticide Programs Pesticide Chemical Search. This database provides links to health effects information and registration status for pesticides.
- Chemistry Dashboard. This database provides information on chemical structures, experimental and predicted physicochemical, and toxicity data.
Critical Effects
Tumor Sites
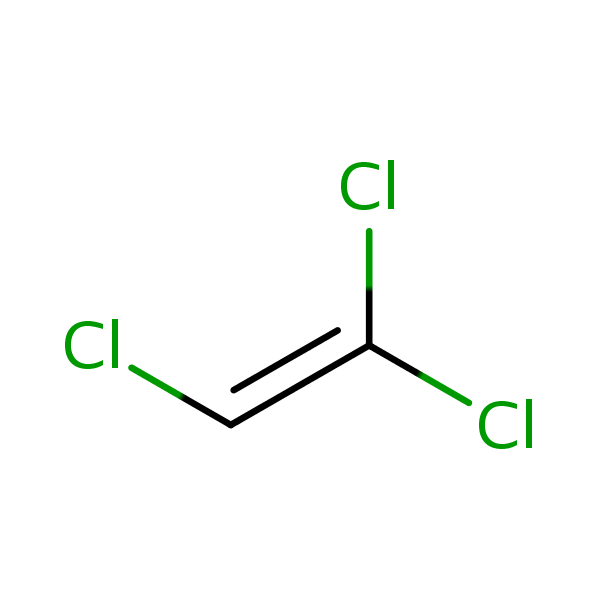
Chemical Structure
Synonyms
- AI3-00052
- Algylen
- Anamenth
- Benzinol
- Caswell No 876
- Cecolene
- Chlorilen
- Chlorylea
- Chorylen
- CirCosolv
- Crawhaspol
- Densinfluat
- Dow-Tri
- Dukeron
- EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 081202
- Ethene, trichloro-
- Ethinyl trichloride
- Ethylene trichloride
- Ethylene, trichloro-
- Fleck-flip
- Flock flip
- Fluate
- Germalgene
- Lanadin
- Lethurin
- NCI-C04546
- NIALK
- NSC 389
- Narcogen
- Narkosoid
- Per-a-clor
- Perm-a-chlor
- Pesticide Code: 081202
- Petzinol
- Philex
- TCE
- Threthylen
- Threthylene
- Trethylene
- Tri
- Tri-Plus M
- Tri-plus
- Triad
- Trial
- Triasol
- Trichloraethen (German)
- Trichloraethylen, tri (German)
- Trichloran
- Trichloren
- Trichlorethene (French)
- Trichlorethylene
- Trichlorethylene, tri (French)
- Trichloroethene
- Trichloroethylene
- Triclene
- Tricloretene (Italian)
- Tricloroetilene (Italian)
- Trielin
- Trielina (Italian)
- Triklone
- Trilene
- Trimar
- Vestrol
- Vitran
- 1,1,2-Trichloroethylene
- 1,1-Dichloro-2-chloroethylene
- 1-Chloro-2,2-dichloroethylene
- 79-01-6