Acrylonitrile
CASRN 107-13-1 | DTXSID5020029
- IRIS Summary (PDF) (23 pp, 162 K)
- Status: Development of the acrylonitrile (re)assessment has been discontinued .
On this page:
Noncancer Assessment
Reference Dose for Oral Exposure (RfD) (PDF) (23 pp, 162 K) Last Updated:
Not assessed under the IRIS Program.
Reference Concentration for Inhalation Exposure (RfC) (PDF) (23 pp, 162 K) Last Updated: 11/01/1991
| System | RfC (mg/m3) | Basis | PoD | Composite UF | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory | 2 x 10 -3 | Degeneration and inflammation of nasal respiratory epithelium; hyperplasia of mucous secreting cells |
LOAEL
(HEC):
1.9
mg/m3 |
1000 | Medium |
Cancer Assessment
Weight of Evidence for Cancer (PDF)
(23 pp, 162 K)
Last Updated: 09/30/1987
| WOE Characterization | Framework for WOE Characterization |
|---|---|
| B1 (Probable human carcinogen - based on limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans) | Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment (U.S. EPA, 1986) |
- The observation of a statistically significant increase in incidence of lung cancer in exposed workers and observation of tumors, generally astrocytomas in the brain, in studies in two rat strains exposed by various routes (drinking water, gavage, and inhalation) forms the basis for this classification.
- This may be a synopsis of the full weight-of-evidence narrative.
Quantitative Estimate of Carcinogenic Risk from Oral Exposure (PDF) (23 pp, 162 K)
Oral Slope Factor:
5.4
x 10-1
per mg/kg-day
Drinking Water Unit Risk:
1.5
x 10-5
per µg/L
Extrapolation Method: Linearized multistage procedure, extra risk
Tumor site(s): Nervous, Other, Gastrointestinal
Tumor type(s): Brain and spinal cord astrocytomas, Zymbal gland carcinomas and stomach papillomas/ carcinomas (Biodynamics, 1980a,b Quast et al., 1980a)
Quantitative Estimate of Carcinogenic Risk from Inhalation Exposure (PDF) (23 pp, 162 K)
Inhalation Unit Risk:
6.8
x 10-5
per µg/m3
Extrapolation Method: Average relative risk
Tumor site(s): Respiratory
Tumor type(s): Respiratory cancer (O'Berg, 1980)
Program Outlook Details
| Public Assessment Materials | Date |
|---|---|
| Discontinued | Dec-2018 |
Note: The acrylonitrile (re)assessment has been discontinued. A new/updated assessment will not be added to the IRIS database at this time.
Chemical Documents
Jun 2011: IRIS Toxicological Review of Acrylonitrile (External Review Draft) (Report)
Mar 2010: IRIS Toxicological Review of Acrylonitrile (Interagency Science Consultation Draft) (Report)
Jul 1987: Health Effects Assessment for Acrylonitrile (Report)
Sep 1985: Health and Environmental Effects Profile for Acrylonitrile (Report)
Oct 1983: Health Assessment Document for Acrylonitrile (Final Report, 1983) (Report)
Other EPA Information
- Human Health Benchmarks for Pesticides (HHBP). This database provides human health benchmarks for pesticides that may be present in drinking water.
- Office of Pesticide Programs Pesticide Chemical Search. This database provides links to health effects information and registration status for pesticides.
- Chemistry Dashboard. This database provides information on chemical structures, experimental and predicted physicochemical, and toxicity data.
Related Links
Critical Effects
Tumor Sites
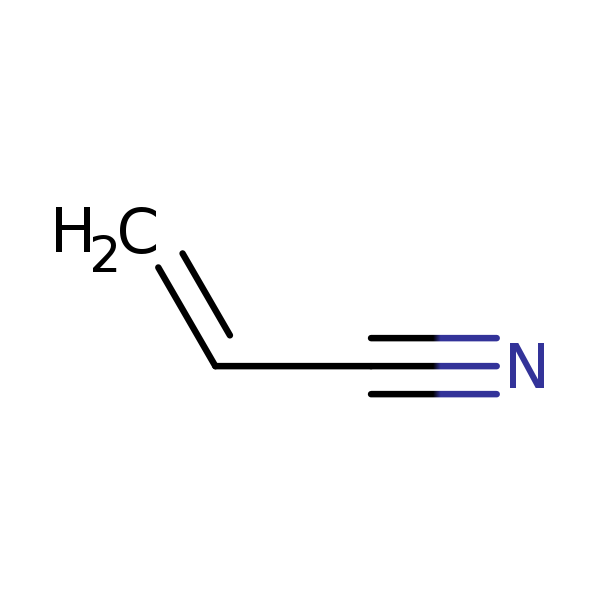
Chemical Structure
Synonyms
- Acritet
- Acrylnitril
- Acrylon
- Acrylonitrile
- Acrylonitrile monomer
- Akrylonitryl
- Carbacryl
- Cianuro di vinile
- Cyanoethylene
- Cyanure de vinyle
- ENT 54
- Fumigrain
- Miller's Fumigrain
- Nitrile acrilico
- Nitrile acrylique
- Propenenitrile
- RCRA Waste Number u009
- TL 314
- UN 1093
- VCN
- Ventox
- Vinyl cyanide
- 107-13-1
- 2-Propenenitrile