1,3-Dichloropropene
CASRN 542-75-6 | DTXSID1022057
- Toxicological Review (PDF) (83 pp, 394 K)
- IRIS Summary (PDF) (34 pp, 213 K)
On this page:
Noncancer Assessment
Reference Dose for Oral Exposure (RfD) (PDF) (34 pp, 213 K) Last Updated: 05/25/2000
| System | RfD (mg/kg-day) | Basis | PoD | Composite UF | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal | 3 x 10 -2 | Chronic irritation |
BMDL
10
:
3.4
mg/kg-day |
100 | High |
Reference Concentration for Inhalation Exposure (RfC) (PDF) (34 pp, 213 K) Last Updated: 05/25/2000
| System | RfC (mg/m3) | Basis | PoD | Composite UF | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory | 2 x 10 -2 | Hypertrophy/ hyperplasia of the nasal respiratory epithelium |
BMCL
10
(HEC):
7.2
x 10-1 mg/m3 |
30 | High |
Cancer Assessment
Weight of Evidence for Cancer (PDF)
(34 pp, 213 K)
Last Updated: 05/25/2000
| WOE Characterization | Framework for WOE Characterization |
|---|---|
| B2 (Probable human carcinogen - based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in animals) | Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment (U.S. EPA, 1986) |
| Known/likely human carcinogen | Proposed Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment (U.S. EPA, 1996) |
- Although the available human data are inadequate, 1,3-dichloropropene is characterized as "likely" to be a human carcinogen in accordance with the Proposed Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment (U.S. EPA, 1996).
- This may be a synopsis of the full weight-of-evidence narrative.
Quantitative Estimate of Carcinogenic Risk from Oral Exposure (PDF) (34 pp, 213 K)
Oral Slope Factor:
1
x 10-1
per mg/kg-day
Drinking Water Unit Risk:
3
x 10-6
per µg/L
Extrapolation Method: Linearized multistage model, extra risk
Tumor site(s): Urinary
Tumor type(s): Urinary bladder carcinoma (NTP, 1985)
Oral Slope Factor:
5
x 10-2
per mg/kg-day
Drinking Water Unit Risk:
2
x 10-6
per µg/L
Extrapolation Method: Linearized multistage model, extra risk
Tumor site(s): Hepatic
Tumor type(s): Hepatocellular adenoma/carcinoma (NTP, 1985)
Oral Slope Factor:
5
x 10-2
per mg/kg-day
Drinking Water Unit Risk:
1
x 10-6
per µg/L
Extrapolation Method: Linearized multistage model, extra risk
Tumor site(s): Hepatic
Tumor type(s): Hepatocellular adenoma/carcinoma (Stott et al., 1995)
Quantitative Estimate of Carcinogenic Risk from Inhalation Exposure (PDF) (34 pp, 213 K)
Inhalation Unit Risk:
4
x 10-6
per µg/m3
Extrapolation Method: Linearized multistage model, extra risk
Tumor site(s): Respiratory
Tumor type(s): Bronchioalveolar adenoma (Lomax et al., 1989)
Other EPA Information
- Human Health Benchmarks for Pesticides (HHBP). This database provides human health benchmarks for pesticides that may be present in drinking water.
- Office of Pesticide Programs Pesticide Chemical Search. This database provides links to health effects information and registration status for pesticides.
- Chemistry Dashboard. This database provides information on chemical structures, experimental and predicted physicochemical, and toxicity data.
Critical Effects
Tumor Sites
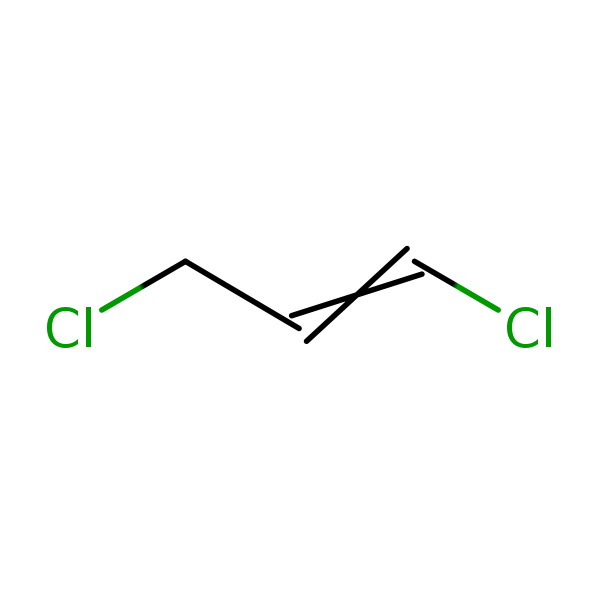
Chemical Structure
Synonyms
- DCP
- Dichloropropene
- Dichloropropene
- Dichloropropene, 1,3-
- NCI-C03985
- Propene, 1,3-dichloro-
- RCRA Waste Number u084
- Telone II
- alpha,gamma-Dichloropropylene
- alpha-Chloroallyl chloride
- gamma-Chloroallyl chloride
- 1,3-Dichloro-2-propene
- 1,3-Dichloropropene
- 1,3-Dichloropropene-1
- 1,3-Dichloropropylene
- 3-Chloroallyl chloride
- 3-Chloropropenyl chloride
- 542-75-6