Epichlorohydrin
CASRN 106-89-8 | DTXSID1020566
- IRIS Summary (PDF) (24 pp, 167 K)
On this page:
Noncancer Assessment
Reference Dose for Oral Exposure (RfD) (PDF) (24 pp, 167 K) Last Updated: 04/01/1992
Information reviewed but value not estimated.
Reference Concentration for Inhalation Exposure (RfC) (PDF) (24 pp, 167 K) Last Updated: 04/01/1992
| System | RfC (mg/m3) | Basis | PoD | Composite UF | Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory | 1 x 10 -3 | Changes in the nasal turbinates |
NOAEL
(HEC):
3.6
x 10-1 mg/m3 |
300 | Medium |
Cancer Assessment
Weight of Evidence for Cancer (PDF)
(24 pp, 167 K)
Last Updated: 03/01/1988
| WOE Characterization | Framework for WOE Characterization |
|---|---|
| B2 (Probable human carcinogen - based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in animals) | Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment (U.S. EPA, 1986) |
- Human data are inadequate. Multiple studies in rats and mice administered epichlorohydrin by various routes were positive. As epichlorohydrin is a strong alkylating agent, tumors are produced at the site of application.
- This may be a synopsis of the full weight-of-evidence narrative.
Quantitative Estimate of Carcinogenic Risk from Oral Exposure (PDF) (24 pp, 167 K)
Oral Slope Factor:
9.9
x 10-3
per mg/kg-day
Drinking Water Unit Risk:
2.8
x 10-7
per µg/L
Extrapolation Method: Linearized multistage procedure, extra risk
Tumor site(s): Gastrointestinal
Tumor type(s): Papillomas and carcinomas of the forestomach (Konishi et al., 1980)
Quantitative Estimate of Carcinogenic Risk from Inhalation Exposure (PDF) (24 pp, 167 K)
Inhalation Unit Risk:
1.2
x 10-6
per µg/m3
Extrapolation Method: Linearized multistage procedure, extra risk
Tumor site(s): Respiratory
Tumor type(s): Nasal cavity tumors (Laskin et al., 1980)
Other EPA Information
- Human Health Benchmarks for Pesticides (HHBP). This database provides human health benchmarks for pesticides that may be present in drinking water.
- Office of Pesticide Programs Pesticide Chemical Search. This database provides links to health effects information and registration status for pesticides.
- Chemistry Dashboard. This database provides information on chemical structures, experimental and predicted physicochemical, and toxicity data.
Critical Effects
Tumor Sites
Chemical Structure
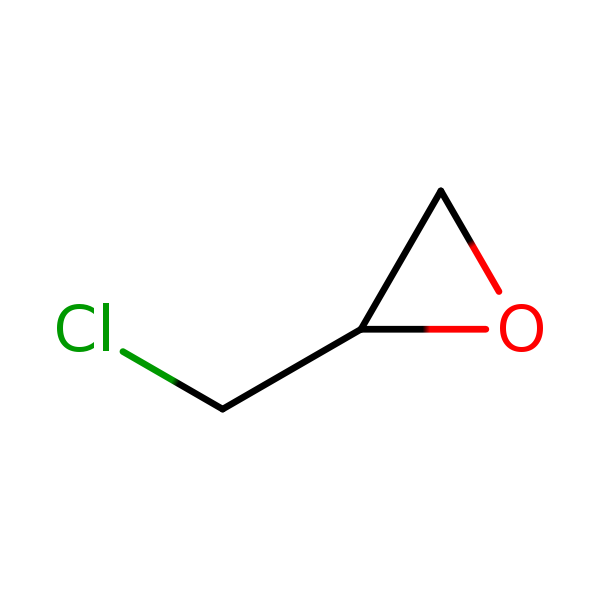
Synonyms
- Chloromethyloxirane
- Epichlorhydrin
- Epichlorohydrin
- y-Chloropropyleneoxide
- 1-Chlor-2,3-epoxypropane
- 106-89-8
- 2-Chloropropylene oxide