Formaldehyde
CASRN 50-00-0 | DTXSID7020637
- Toxicological Review (PDF) (927 pp, 16.3 MB, about PDF)
- IRIS Executive Summary (PDF) (10 pp, 450.2 KB, about PDF)
Statistical Inferences from Formaldehyde Dna-Protein Cross-Link Data
On this page:
Alert
Notice - This site contains archived material(s)
Archive disclaimer
Archived files are provided for reference purposes only.
The file was current when produced, but is no longer maintained and may now be outdated.
Persons with disabilities having difficulty accessing archived files may contact the IRIS Webmaster for assistance.
Please use the contact us form if you need additional support.
Overview
Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling has reached considerable sophistication in its application in the pharmacological and environmental health areas. Yet, mature methodologies for making statistical inferences have not been routinely incorporated in these applications except in a few data-rich cases. In this paper, we work with a previously developed PBPK model for the formation and disposition of DNA-protein cross-links formed by inhaled formaldehyde in the nasal lining of rats and rhesus monkeys and provide improved statistical inference on estimated model parameters. We purposefully choose this model because it is based on sparse time course data.Related Links
Critical Effect Systems
Tumor Sites
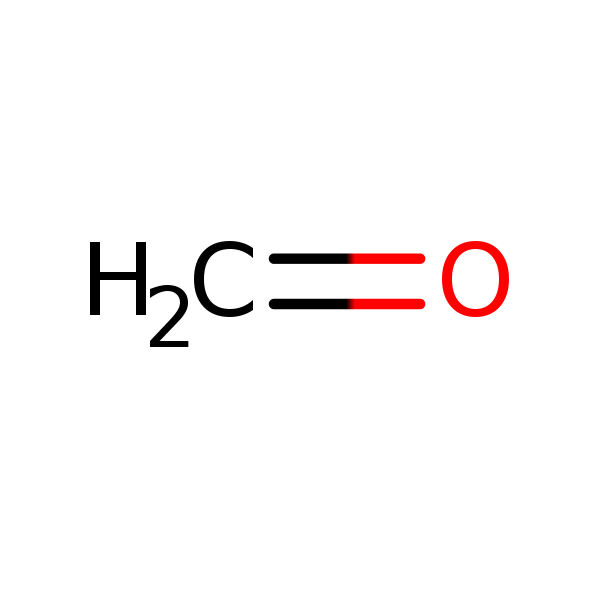
Chemical Structure for
Formaldehyde
Synonyms
- Aldehyd mravenci (Czech)
- Aldehyde formique (French)
- Aldeide formica (Italian)
- BFV
- FA
- Formaldehyd (Czech, Polish)
- Formaldehyde
- Formaldehyde solution (DOT)
- Formalin
- Formalith
- Formic aldehyde
- Formol
- Fyde
- Hoch
- Ivalon
- Karsan
- Lysoform
- Methanal
- Methyl aldehyde
- Methylene glycol
- Methylene oxide
- Morbicid
- NCI-C02799
- Oplossingen (Dutch)
- Oxomethane
- Oxymethylene
- Paraform
- Polyoxymethylene glycols
- RCRA Waste Number U122
- Superlysoform
- UN 1198 (DOT)
- UN 2209 (DOT)
- 50-00-0