Diethyl phthalate (DEP)
CASRN 84-66-2 | DTXSID7021780
- IRIS Summary (PDF) (10 pp, 100.6 KB, about PDF)
- Status: Development of the diethyl phthalate (dep) (re)assessment has been discontinued.
IRIS Toxicological Review of Diethyl Phthalate (DEP) (Preliminary Assessment Materials)
On this page:
Alert
Notice - This site contains archived material(s)
Archive disclaimer
Archived files are provided for reference purposes only.
The file was current when produced, but is no longer maintained and may now be outdated.
Persons with disabilities having difficulty accessing archived files may contact the IRIS Webmaster for assistance.
Please use the contact us form if you need additional support.
Overview
In March 2014, EPA released the draft literature searches and associated search strategies, evidence tables, and exposure response arrays for DEP to obtain input from stakeholders and the public prior to developing the draft IRIS assessment. Specifically, EPA was interested in comments on the following:- Draft literature search strategies
- The approach for identifying studies
- The screening process for selecting pertinent studies
- The resulting list of pertinent studies
- Preliminary evidence tables
- The process for selecting studies to include in evidence tables
- The quality of the studies in the evidence tables
Background
DEP is a colorless liquid with slight aromatic odor. It is soluble in water and slightly volatile. Impurities in technical DEP include isophthalic acid, terephthalic acid and maleic anhydride at levels of less than 1%. The DEP molecule contains two “ester” chemical groups. Ester chemical groups are generally susceptible to being hydrolyzed by a number of biotic and abiotic processes. Cleaving one DEP ester group leads to the formation of a monoester (monethyl phthalate – MEP) and cleaving both ester groups produces the diacid metabolite/degradate, phthalic acid.DEP is used to improve the performance and durability of a number of products. As a plasticizer, it is added to plastic polymers to help maintain flexibility. It has been used in a variety of products including plastic films, rubber, tape, toothbrushes, automotive components, tool handles and toys. In addition to plastics, DEP is present in a wide range of personal care products (e.g., cosmetics, perfume, hair spray, nail polish, soap, detergent, and lotions), industrial materials (e.g., rocket propellant, dyes, packaging, sealants and lubricants), and medical products (e.g., enteric coatings on tablets and in dental impression materials). Previous uses as an inert ingredient in pesticide formulations are no longer allowed in the U.S.
| Date | Description |
|---|---|
| Mar 2014 | EPA released Preliminary Assessment Materials (draft literature searches and associated search strategies, evidence tables and exposure response arrays) in anticipation for discussion at an upcoming IRIS Public Science Meeting. |
| Apr 2014 | EPA discussed DEP at the April 2014 IRIS public science meeting. |
Download(s)
This download(s) is distributed solely for the purpose of pre-dissemination peer review under applicable information quality guidelines. It has not been formally disseminated by EPA. It does not represent and should not be construed to represent any Agency determination or policy.
- Scoping information, preliminary literature search, associated strategy and evidence tables for DEP (PDF) (129 pp, 1.9 MB, about PDF)
- Primary literature search references sorted by author (DEP) (dynamic literature link - generated by HERO, leaving the IRIS website)
- Targeted literature search for epidemiological references sorted by author (DEP) (dynamic literature link - generated by HERO, leaving the IRIS website)
- Literature selection process for the DEP primary literature (dynamic literature link - generated by HERO, leaving the IRIS website)
- Literature selection process for the DEP targeted epidemiological literature (dynamic literature link - generated by HERO, leaving the IRIS website)
- IRIS April 2014 Meeting & Presentations
If you have a disability and the format of any material on our web pages interferes with your ability to access the information, please reach out to us using the Contact Us about IRIS form for assistance. To enable us to respond in a manner most helpful to you, please indicate the nature of the accessibility problem, the web address of the requested material, your preferred format in which you want to receive the material (electronic format (ASCII, etc.), standard print, large print, etc.), and your contact information.
Related Links
Chemical Structure for
Diethyl phthalate (DEP)
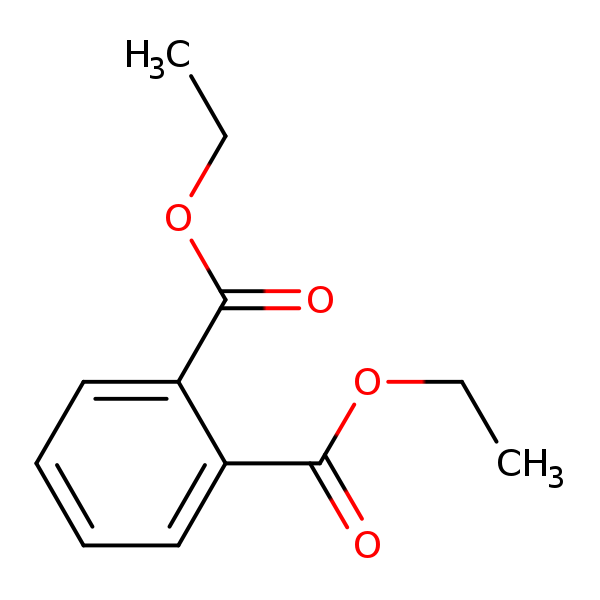
Synonyms
- Anozol
- DPX-f5384
- Diethyl phthalate
- Estol 1550
- Ethyl phthalate
- NCI-C60048
- Neantine
- Palatinol A
- Phthalol
- Phthalsaeurediaethylester
- Placidol E
- RCRA Waste Number u088
- 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, diethyl ester
- 84-66-2
